Raspberry Pi: Porovnání verzí
Bez shrnutí editace |
|||
| (Není zobrazeno 34 mezilehlých verzí od stejného uživatele.) | |||
| Řádek 4: | Řádek 4: | ||
|- style="vertical-align: top;" | |- style="vertical-align: top;" | ||
| | | | ||
http://www.youtube.com/user/RaspberryPiTutorials/videos | |||
http://www.youtube.com/user/RaspberryPiBeginners/videos?flow=grid&view=0 | |||
Soutěž [[NAG-IoE]] | Soutěž [[NAG-IoE]] | ||
[[Soubor:NAG-IoE.png|300px|NAG-IoE|link=NAG-IoE]] | [[Soubor:NAG-IoE.png|300px|NAG-IoE|link=NAG-IoE]] | ||
[[Soubor:raspberry_03.jpg|200px|link=https://magpi.raspberrypi.com/books/beginners-guide-4th-ed/|MagPi - A Magazine for Raspberry Pi Users]] | |||
[[Soubor:PDF.gif]] [https://magazines-attachments.raspberrypi.org/books/full_pdfs/000/000/038/original/BeginnersGuide-4thEd-Eng_v2.pdf Beginners Guide] | |||
[[Soubor:Raspberry_Pi_3.png|300px|link=https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/raspberry-gpio Sparkfun|Raspberry gPIo]] | |||
[[Soubor:Raspberry_Pi_2.png|300px|link=http://www.zive.cz/clanky/vyzkouseli-jsme-mikropocitac-raspberry-pi/sc-3-a-165391/default.aspx#utm_medium=selfpromo&utm_source=avmania&utm_campaign=RSSfeed|Živě - Vyzkoušeli jsme mikropočítač Raspberry Pi]] | |||
[[Soubor:raspberry_02.jpg|200px|link=http://mcu.cz/news.php?extend.3176.3|RaspberryPi - ovládání GPIO přes web]] | |||
|} | |} | ||
== IoT UPJŠ == | |||
DU: shlédnou videa (alt. z jiných zdrojů) o Raspberry. https://youtu.be/fdBSbarhAUY https://youtu.be/0VwchnogzuQ | |||
Potvrďte splnění | |||
{{#widget:YouTube|id=fdBSbarhAUY|height=270|width=360|IoT UPJŠ - Základy IoT - Raspberry Pi - 1. intro, Raspbian, SSH, VNC|right}} | |||
{{#widget:YouTube|id=0VwchnogzuQ|height=270|width=360|IoT UPJŠ - Základy IoT - Raspberry Pi - 2. GPIO, WiringPi, I2C|right}} | |||
VNC: ssh pi@192.168.1.238 | |||
ifconfig | |||
sudo raspi.config | |||
rasbian na PC | |||
== Python == | |||
[[Soubor:RpiPython_03_PINOUT.png|300px|right|link=https://pinout.xyz/|Raspberry Pi GPIO Pinout]] | |||
[[Soubor:PDF.gif]] [https://blog.withcode.uk/wp-content/uploads/2016/10/RPi_GPIO_python_quickstart_guide.pdf Raspberry Pi Python GPIO Quick start guide] | |||
install GPIO: sudo apt-get install python-rpi.gpio python3-rpi.gpio | |||
Install library: | |||
sudo apt-get install python-rpi.gpio python3-rpi.gpio | |||
Running the Script: | |||
sudo python blinker.py | |||
[[Soubor:RpiPython_01.png|300px]][[Soubor:RpiPython_02.png|300px]] | |||
===RPi.GPIO === | |||
<source lang="Python"> | |||
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO | |||
from time import sleep | |||
GPIO.setwarnings(False) | |||
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD) | |||
GPIO.setup(18, GPIO.OUT, initial=GPIO.LOW) | |||
while True: | |||
GPIO.output (18, GPIO.HIGH) | |||
sleep(0.2) | |||
GPIO.output (18, GPIO.LOW) | |||
sleep (0.2) | |||
</source> | |||
[https://create.withcode.uk/ create.withcode.uk] | |||
[[Soubor:RpiPython_03.png|300px|link=https://create.withcode.uk/]] | |||
===gpiozero=== | |||
Source: https://automaticaddison.com/how-to-blink-an-led-on-raspberry-pi-3-model-b/ | |||
<source lang="Python"> | |||
import gpiozero # The GPIO library for Raspberry Pi | |||
import time # Enables Python to manage timing | |||
led = gpiozero.LED(17) # Reference GPIO17 | |||
while True: | |||
led.on() # Turn the LED on | |||
time.sleep(1) | |||
led.off() # Turn the LED off | |||
time.sleep(1) # Pause for 1 second | |||
</source> | |||
[https://create.withcode.uk/ create.withcode.uk] | |||
[[Soubor:RpiPython_04.png|300px|link=https://create.withcode.uk/]] | |||
=== BOARD vs BCM === | |||
source: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/raspberry-gpio#python-rpigpio-example | |||
<source lang="Python"> | |||
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO # External module imports | |||
import time | |||
# Pin Definitons: | |||
ledPin = 23 # GPIO 23 = pin 16 | |||
butPin = 17 # GPIO 17 = pin 11 | |||
# choose BOARD or BCM | |||
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) # BCM for GPIO numbering | |||
# GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD) # BOARD for header pin numbering | |||
GPIO.setwarnings(False) | |||
GPIO.setup(ledPin, GPIO.OUT) # LED pin set as output GPIO.setup(23, GPIO.OUT) | |||
# GPIO.setup(butPin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP) # Button pin set as input w/ pull-up | |||
GPIO.setup(butPin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_DOWN) # Button pin set as input w/ pull-down | |||
# Initial state for LEDs: | |||
GPIO.output(ledPin, GPIO.LOW) # GPIO.output(23, 0) = GPIO.output(23, False) | |||
time.sleep(0.1) # wait 0,1 s | |||
GPIO.output(ledPin, GPIO.HIGH) # GPIO.output(23, 1) = GPIO.output(23, True) | |||
time.sleep(0.1) # wait 0,1 s | |||
while True: | |||
# print("Here we go! Press CTRL+C to exit") | |||
# try: | |||
# while 1: | |||
if GPIO.input(butPin): # button is released | |||
GPIO.output(ledPin, GPIO.LOW) | |||
else: # button is pressed: | |||
GPIO.output(ledPin, GPIO.HIGH) | |||
time.sleep(0.075) | |||
GPIO.output(ledPin, GPIO.LOW) | |||
time.sleep(0.075) | |||
# except KeyboardInterrupt: # If CTRL+C is pressed, exit cleanly: | |||
GPIO.cleanup() # cleanup all GPIO | |||
</source> | |||
http:// | ===blink.py=== | ||
source: /opt/nagioe/python_demo/blink.py | |||
<source lang="Python"> | |||
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO | |||
import time | |||
def blink(pin): # blinking function | |||
GPIO.output(pin,GPIO.HIGH) | |||
time.sleep(1) | |||
GPIO.output(pin,GPIO.LOW) | |||
time.sleep(1) | |||
return | |||
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD) # to use Raspberry Pi board pin numbers | |||
GPIO.setwarnings(False) | |||
GPIO.setup(11, GPIO.OUT) # set up GPIO output channel | |||
for i in range(0,50): | |||
blink(11) | |||
GPIO.cleanup() | |||
</source> | |||
===push.py=== | |||
source: /opt/nagioe/python_demo/push.py | |||
<source lang="Python"> | |||
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO | |||
import time | |||
print GPIO.RPI_REVISION | |||
print GPIO.VERSION | |||
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD) | |||
pin=40 | |||
GPIO.setup(pin, GPIO.IN) | |||
GPIO.setup(pin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP) | |||
while (1): | |||
print GPIO.input(pin) | |||
time.sleep(0.5) | |||
#GPIO.output(pin, False) | |||
GPIO.cleanup() | |||
</source> | |||
=== Control LED === | |||
<source lang="Python"> | |||
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO | |||
import time | |||
def blink(pin, pin2): # blinking function | |||
GPIO.output(pin,GPIO.HIGH) | |||
time.sleep(0.1) | |||
GPIO.output(pin,GPIO.LOW) | |||
time.sleep(0.1) | |||
GPIO.output(pin2,GPIO.HIGH) | |||
time.sleep(0.1) | |||
GPIO.output(pin2,GPIO.LOW) | |||
time.sleep(0.1) | |||
return | |||
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD) # to use Raspberry Pi board pin numbers | |||
GPIO.setwarnings(False) | |||
GPIO.setup(11, GPIO.OUT) # set up GPIO output channel | |||
GPIO.setup(13, GPIO.OUT) | |||
GPIO.setup(40, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP) | |||
blink(11, 13) | |||
while (1): | |||
if GPIO.input(40) == 0: | |||
blink(11, 13) | |||
time.sleep(0.1) | |||
GPIO.cleanup() | |||
</source> | |||
=== Turn LED === | |||
source: http://engr.uconn.edu/~song/classes/nes/RPi.pdf | |||
<source lang="Python"> | |||
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO | |||
import time | |||
def main(): | |||
GPIO.cleanup() | |||
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD) # to use Raspberry Pi board pin numbers | |||
GPIO.setup(11, GPIO.OUT) # set up GPIO output channel | |||
while True: | |||
GPIO.output(11, GPIO.LOW) # set RPi board pin 11 low. Turn off LED. | |||
time.sleep(1) | |||
GPIO.output(11, GPIO.HIGH) # set RPi board pin 11 high. Turn on LED. | |||
time.sleep(2) | |||
main() | |||
</source> | |||
== Wiring Pi == | |||
[[Soubor:RBP_Pinout.png|300px|link=https://pinout.xyz/pinout/wiringpi/]] | |||
{{#widget:YouTube|id=J6KsTz6hjfU|height=270|width=360|Popis|right}} | |||
===[http://wiringpi.com/examples/blink/ Blink]=== | |||
[[Soubor:RB_LED.png|300px|link=http://wiringpi.com/examples/blink/]] | |||
<source lang"C"> | |||
#include <wiringPi.h> | |||
int main (void) | |||
{ | |||
wiringPiSetup () ; | |||
pinMode (0, OUTPUT) ; | |||
for (;;) | |||
{ | |||
digitalWrite (0, HIGH) ; | |||
delay (500) ; | |||
digitalWrite (0, LOW) ; | |||
delay (500) ; | |||
} | |||
return 0 ; | |||
} | |||
</source> | |||
To compile and run: | |||
gcc -Wall -o blink blink.c -lwiringPi | |||
sudo ./blink | |||
=== Set up the ports === | |||
[ | [[soubor:RB2_LED-PUSCH-SERVO.png|400px]] | ||
[ | [http://raspi.tv/2013/how-to-use-wiringpi2-for-python-on-the-raspberry-pi-in-raspbian How to use WiringPi2 for Python on the Raspberry Pi in Raspbian part 1] | ||
<source lang"C"> | |||
# GPIO port numbers | |||
import wiringpi2 as wiringpi | |||
wiringpi.wiringPiSetupGpio() | |||
wiringpi.pinMode(25, 0) # sets GPIO 25 to input | |||
wiringpi.pinMode(24, 1) # sets GPIO 24 to output | |||
wiringpi.pinMode(18, 2) # sets GPIO 18 to PWM mode | |||
# wiringpi numbers | |||
import wiringpi2 as wiringpi | |||
wiringpi.wiringPiSetup() | |||
wiringpi.pinMode(6, 0) # sets WP pin 6 to input | |||
wiringpi.pinMode(5, 1) # sets WP pin 5 to output | |||
wiringpi.pinMode(1, 2) # sets WP pin 1 to PWM mode | |||
# Physical P1 header pin numbers | |||
import wiringpi2 as wiringpi | |||
wiringPiSetupPhys() | |||
wiringpi.pinMode(22, 0) # sets P1 pin 22 to input | |||
wiringpi.pinMode(18, 1) # sets P1 pin 18 to output | |||
wiringpi.pinMode(12, 2) # sets P1 pin 12 to PWM mode | |||
</source> | |||
== RaspBian == | |||
Username: pi, password: NAGIoE2015 | |||
Re-mapping Keyboard: XKBLAYOUT=”gb” Change “gb” to “us” | |||
sudo vi /etc/default/keyboard | |||
Start the desktop by typing: (http://engr.uconn.edu/~song/classes/nes/RPi.pdf) | |||
startx | |||
Booting your Raspberry Pi for the first time | |||
sudo raspi-config | |||
Update apt-get package index files: | |||
sudo apt-get update | |||
Install SSH: | |||
sudo apt-get install ssh | |||
Start SSH server: | |||
sudo /etc/init.d/ssh start | |||
To start the SSH server every time the Pi boots up: | |||
sudo update-rc.d ssh defaults | |||
[http://www.raspberrypi-spy.co.uk/2014/05/how-to-autostart-apps-in-rasbian-lxde-desktop/ How To Autostart Apps In Rasbian LXDE Desktop] | |||
sudo nano /etc/xdg/lxsession/LXDE-pi/autostart | |||
Auto-run Python Scripts | |||
@/usr/bin/python /home/pi/example.py | |||
Aktuální verze z 10. 2. 2022, 18:00
| NAG-IoE | |
|
http://www.youtube.com/user/RaspberryPiTutorials/videos http://www.youtube.com/user/RaspberryPiBeginners/videos?flow=grid&view=0 Soutěž NAG-IoE
| |
IoT UPJŠ
DU: shlédnou videa (alt. z jiných zdrojů) o Raspberry. https://youtu.be/fdBSbarhAUY https://youtu.be/0VwchnogzuQ Potvrďte splnění
VNC: ssh pi@192.168.1.238 ifconfig
sudo raspi.config
rasbian na PC
Python
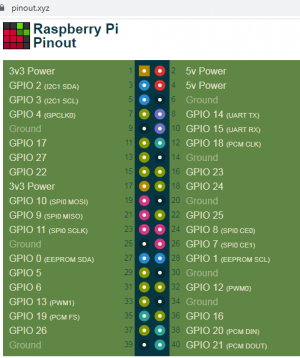
![]() Raspberry Pi Python GPIO Quick start guide
Raspberry Pi Python GPIO Quick start guide
install GPIO: sudo apt-get install python-rpi.gpio python3-rpi.gpio
Install library:
sudo apt-get install python-rpi.gpio python3-rpi.gpio
Running the Script:
sudo python blinker.py
RPi.GPIO
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
from time import sleep
GPIO.setwarnings(False)
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD)
GPIO.setup(18, GPIO.OUT, initial=GPIO.LOW)
while True:
GPIO.output (18, GPIO.HIGH)
sleep(0.2)
GPIO.output (18, GPIO.LOW)
sleep (0.2)
gpiozero
Source: https://automaticaddison.com/how-to-blink-an-led-on-raspberry-pi-3-model-b/
import gpiozero # The GPIO library for Raspberry Pi
import time # Enables Python to manage timing
led = gpiozero.LED(17) # Reference GPIO17
while True:
led.on() # Turn the LED on
time.sleep(1)
led.off() # Turn the LED off
time.sleep(1) # Pause for 1 second
BOARD vs BCM
source: https://learn.sparkfun.com/tutorials/raspberry-gpio#python-rpigpio-example
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO # External module imports
import time
# Pin Definitons:
ledPin = 23 # GPIO 23 = pin 16
butPin = 17 # GPIO 17 = pin 11
# choose BOARD or BCM
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BCM) # BCM for GPIO numbering
# GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD) # BOARD for header pin numbering
GPIO.setwarnings(False)
GPIO.setup(ledPin, GPIO.OUT) # LED pin set as output GPIO.setup(23, GPIO.OUT)
# GPIO.setup(butPin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP) # Button pin set as input w/ pull-up
GPIO.setup(butPin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_DOWN) # Button pin set as input w/ pull-down
# Initial state for LEDs:
GPIO.output(ledPin, GPIO.LOW) # GPIO.output(23, 0) = GPIO.output(23, False)
time.sleep(0.1) # wait 0,1 s
GPIO.output(ledPin, GPIO.HIGH) # GPIO.output(23, 1) = GPIO.output(23, True)
time.sleep(0.1) # wait 0,1 s
while True:
# print("Here we go! Press CTRL+C to exit")
# try:
# while 1:
if GPIO.input(butPin): # button is released
GPIO.output(ledPin, GPIO.LOW)
else: # button is pressed:
GPIO.output(ledPin, GPIO.HIGH)
time.sleep(0.075)
GPIO.output(ledPin, GPIO.LOW)
time.sleep(0.075)
# except KeyboardInterrupt: # If CTRL+C is pressed, exit cleanly:
GPIO.cleanup() # cleanup all GPIO
blink.py
source: /opt/nagioe/python_demo/blink.py
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
def blink(pin): # blinking function
GPIO.output(pin,GPIO.HIGH)
time.sleep(1)
GPIO.output(pin,GPIO.LOW)
time.sleep(1)
return
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD) # to use Raspberry Pi board pin numbers
GPIO.setwarnings(False)
GPIO.setup(11, GPIO.OUT) # set up GPIO output channel
for i in range(0,50):
blink(11)
GPIO.cleanup()
push.py
source: /opt/nagioe/python_demo/push.py
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
print GPIO.RPI_REVISION
print GPIO.VERSION
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD)
pin=40
GPIO.setup(pin, GPIO.IN)
GPIO.setup(pin, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
while (1):
print GPIO.input(pin)
time.sleep(0.5)
#GPIO.output(pin, False)
GPIO.cleanup()
Control LED
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
def blink(pin, pin2): # blinking function
GPIO.output(pin,GPIO.HIGH)
time.sleep(0.1)
GPIO.output(pin,GPIO.LOW)
time.sleep(0.1)
GPIO.output(pin2,GPIO.HIGH)
time.sleep(0.1)
GPIO.output(pin2,GPIO.LOW)
time.sleep(0.1)
return
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD) # to use Raspberry Pi board pin numbers
GPIO.setwarnings(False)
GPIO.setup(11, GPIO.OUT) # set up GPIO output channel
GPIO.setup(13, GPIO.OUT)
GPIO.setup(40, GPIO.IN, pull_up_down=GPIO.PUD_UP)
blink(11, 13)
while (1):
if GPIO.input(40) == 0:
blink(11, 13)
time.sleep(0.1)
GPIO.cleanup()
Turn LED
source: http://engr.uconn.edu/~song/classes/nes/RPi.pdf
import RPi.GPIO as GPIO
import time
def main():
GPIO.cleanup()
GPIO.setmode(GPIO.BOARD) # to use Raspberry Pi board pin numbers
GPIO.setup(11, GPIO.OUT) # set up GPIO output channel
while True:
GPIO.output(11, GPIO.LOW) # set RPi board pin 11 low. Turn off LED.
time.sleep(1)
GPIO.output(11, GPIO.HIGH) # set RPi board pin 11 high. Turn on LED.
time.sleep(2)
main()
Wiring Pi
Blink
#include <wiringPi.h>
int main (void)
{
wiringPiSetup () ;
pinMode (0, OUTPUT) ;
for (;;)
{
digitalWrite (0, HIGH) ;
delay (500) ;
digitalWrite (0, LOW) ;
delay (500) ;
}
return 0 ;
}To compile and run:
gcc -Wall -o blink blink.c -lwiringPi sudo ./blink
Set up the ports
How to use WiringPi2 for Python on the Raspberry Pi in Raspbian part 1
# GPIO port numbers
import wiringpi2 as wiringpi
wiringpi.wiringPiSetupGpio()
wiringpi.pinMode(25, 0) # sets GPIO 25 to input
wiringpi.pinMode(24, 1) # sets GPIO 24 to output
wiringpi.pinMode(18, 2) # sets GPIO 18 to PWM mode
# wiringpi numbers
import wiringpi2 as wiringpi
wiringpi.wiringPiSetup()
wiringpi.pinMode(6, 0) # sets WP pin 6 to input
wiringpi.pinMode(5, 1) # sets WP pin 5 to output
wiringpi.pinMode(1, 2) # sets WP pin 1 to PWM mode
# Physical P1 header pin numbers
import wiringpi2 as wiringpi
wiringPiSetupPhys()
wiringpi.pinMode(22, 0) # sets P1 pin 22 to input
wiringpi.pinMode(18, 1) # sets P1 pin 18 to output
wiringpi.pinMode(12, 2) # sets P1 pin 12 to PWM modeRaspBian
Username: pi, password: NAGIoE2015
Re-mapping Keyboard: XKBLAYOUT=”gb” Change “gb” to “us”
sudo vi /etc/default/keyboard
Start the desktop by typing: (http://engr.uconn.edu/~song/classes/nes/RPi.pdf)
startx
Booting your Raspberry Pi for the first time
sudo raspi-config
Update apt-get package index files:
sudo apt-get update
Install SSH:
sudo apt-get install ssh
Start SSH server:
sudo /etc/init.d/ssh start
To start the SSH server every time the Pi boots up:
sudo update-rc.d ssh defaults
How To Autostart Apps In Rasbian LXDE Desktop
sudo nano /etc/xdg/lxsession/LXDE-pi/autostart
Auto-run Python Scripts
@/usr/bin/python /home/pi/example.py











